

4 October, 2021
32 Hours Online + 18 Hours Homework
€ 2450
Financing is all about the free interplay of market forces. The parties on the demand side are companies. However, companies are very diverse. A small start-up company does not have the same financing requirements as a long-established, internationally operating business. However, the parties on the supply side are diverse as well. A bank, for instance, will need to be approached entirely differently from a venture capital fund or a business angel. In order to optimise the interplay of supply and demand and achieve the best possible financing and financing terms, a good understanding of the company’s needs, on the one hand, and the different suppliers, on the other, is essential.
This course aims at giving insights in the principles of financial management. The theoretical insights are systematically illustrated by concrete cases and exercises. During the course alternative scenarios will be discussed.
By the end of this course, participants should be capable to advice, in a fast and accurate way, on a difficult, hybrid, financing structure.
The course is especially interesting for students, financial managers (CFO), bankers, venture capitalists and entrepreneurs and start-ups.
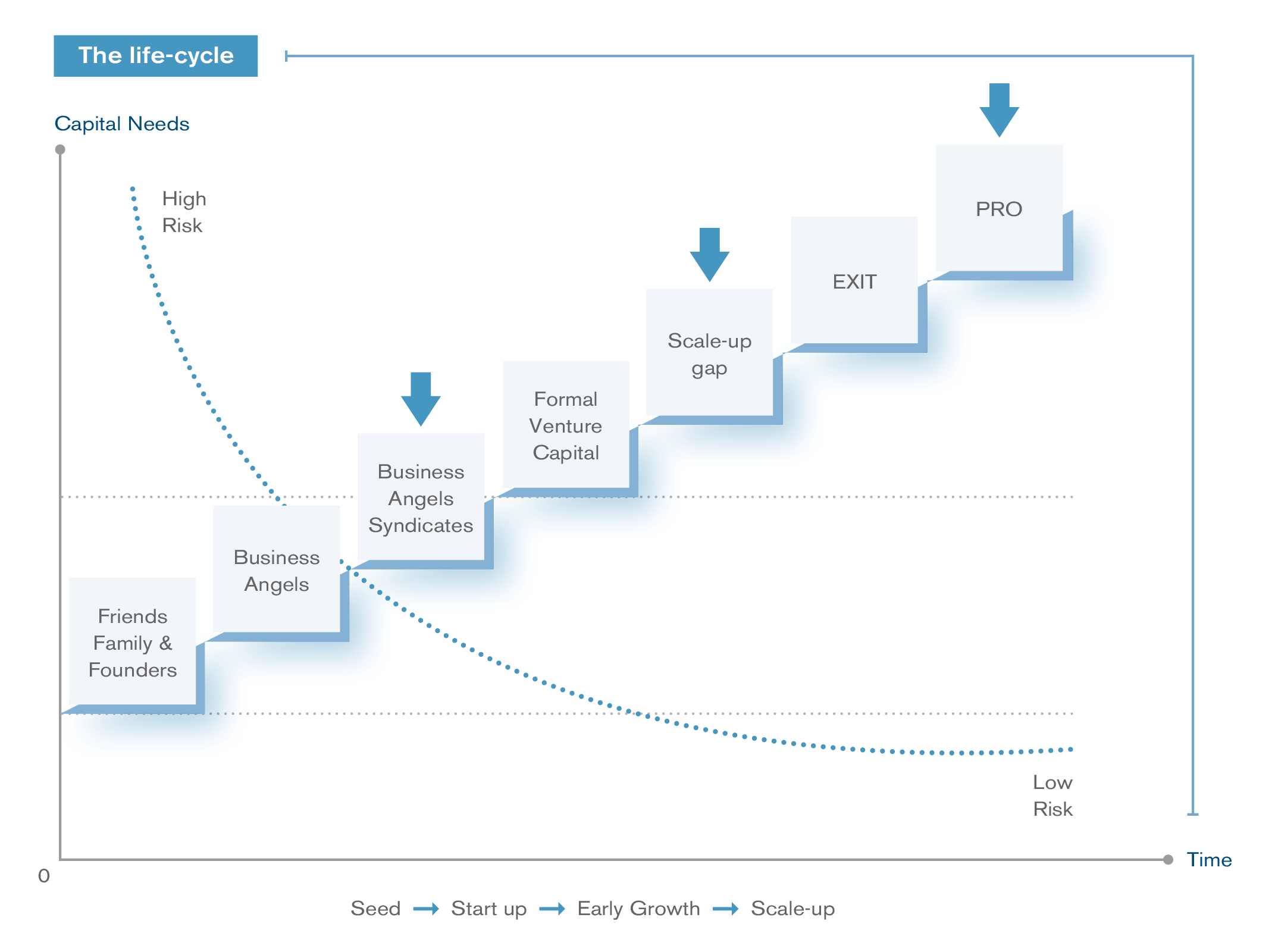
Companies tend to express their financing needs in terms of a sum of money. Their need, however, is not only for a certain amount, but may also relate to the form, the time limit and the arrangements of the financing. It therefore seems useful, first of all, to present an overview of the advantages and disadvantages of the various financing arrangements. Every form of financing has its advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to find the optimal solution as not all the money is the same.
Presentation by the lecturer: 60 min
Zoom breakout session — Getting to know each other and sharing experiences: 15 min
Q&A: 45 min
The valuation of a company is important, as the financial function is focused on enhancing the value of the company. It is, therefore, interesting to get a clear idea of that value. Beyond this context as well, it can be important to be able to determine the value of the company. For an investor, for example, this is important in deciding on the purchase of shares. He or she has to know whether the invested amount will generate sufficient dividends and/ or capital gains in the event of a sale before he or she can consider the investment as interesting. In the event of a sale, liquidation or succession, the valuation of a company is also extremely important. With regard to financing, valuation is particularly significant for equity financing. Equity financing means that the company is financed by a third party, who receives in return for the financed amount a share of equity of the company. The number of shares, or the percentage of shares, attributable to this external financier, depends on the estimated value of the company.
Presentation by the lecturer: 60 min
Zoom breakout session — Getting to know each other and sharing experiences: 15 min
Q&A: 45 min
Debt financing remains the major source of financing of companies. Debt financing is an action between at least two parties: the lender and the borrower. Whereas in commercial transactions a credit transaction is a precondition of the transaction, in financial transactions it is the centre of the operation. The borrower has to decide whether and to what extent he wants to rely on credit, in what form and for how long. The lender, for his part, will investigate whether he is willing to grant credit, under what form and on what terms. Furthermore, he will figure out how he can protect himself against possible default.
Presentation by the lecturer: 60 min
Zoom breakout session — Getting to know each other and sharing experiences: 15 min
Q&A: 45 min
The term ‘venture’ is derived from ‘adventure’, which means taking a risk. Usually not only money is invested. Experience, connections, technical skills and management knowledge can also be offered to the company. Venture capital is increasingly considered as a ‘deus ex machina’ for all financing difficulties. Should the bank refuse credit, then venture capitalists offer the solution. Besides, progressive bankers switch to venture capital funds. But what is venture capital exactly?
Presentation by the lecturer: 60 min
Zoom breakout session — Getting to know each other and sharing experiences: 15 min
Q&A: 45 min
An alternative to financing a company start-up with formal venture capital is the so- called ‘informal venture capital’. Informal and formal venture capital are two totally different markets with different market players and a different perception. One of the consequences is that the informal venture capitalist is far more interested in the start-up enterprise than the formal venture capitalist is.
Presentation by the lecturer: 60 min
Zoom breakout session — Getting to know each other and sharing experiences: 15 min
Q&A: 45 min
Love and money seldom go hand in hand, they are more like Eros and Thanatos. When money is involved, emotions are better set aside. And yet, there are exceptions to this universal rule. After all, financial backers can be moved to finance starters in particular because they have an affective relationship with the founder.
Presentation by the lecturer: 60 min
Zoom breakout session — Getting to know each other and sharing experiences: 15 min
Q&A: 45 min
The stock exchange or a public listing of the shares can either be a source for attracting new financing resources or allowing certain investors to realise their exit. For a lot of risk capitalists, a listing of their investee is the ideal exit. In case of a first stock exchange listing, we speak about an IPO. Listed companies can, of course, implement a capital increase through the stock exchange by issuing new shares and in this way collect additional financial resources. But the listing does not only offer benefits. Some listed companies prefer to be no longer be publicly listed and then we are talking about delisting.
One of the reasons for delisting is the financial regulation. Regulation is needed but has an impact on enterprises and financing, in particular the Basel agreements.
Presentation by the lecturer: 60 min
Zoom breakout session — Getting to know each other and sharing experiences: 15 min
Q&A: 45 min
Entrepreneurs-in-Residence accepted for the WIPA Start-up Exchange Programmes are awarded a professional certificate featuring their proficiency level on global entrepreneurship and a personal WIPA Identity Card.